The official foreign trade website of Hongbai Technology has been officially launched!


Explanation of stud welding terms
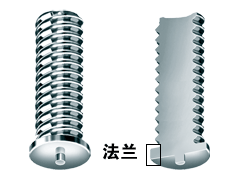 A flange refers to a raised edge around the front end of a stud. Usually, energy storage studs and short-cycle studs have flanges, while long-cycle studs do not.
A flange refers to a raised edge around the front end of a stud. Usually, energy storage studs and short-cycle studs have flanges, while long-cycle studs do not.
Since the molten pools in energy storage stud welding and short-cycle stud welding are relatively shallow, the presence of the flange edge can increase the welding cross-sectional area and improve the welding strength of the stud.
The phenomenon that the arc column of the arc deviates from the stud axis is called the arc blow phenomenon.

The picture shows the magnetic blow phenomenon that occurs during short-cycle pulsed arc welding.
When arc blow occurs, one side of the stud will melt intensely, resulting in little or almost no weld on one side of the stud, while the weld on the other side is excessive, accompanied by the generation of pores. It may even cause the stud to be non – vertical, easily burn out the collet, and may also affect the welding strength.
Arc blow mostly occurs during long – cycle drawn arc stud welding. It hardly occurs in energy – storage stud welding and rarely occurs in short – cycle drawn arc stud welding. The longer the welding time, the greater the possibility of arc blow.
The following reasons may cause arc blow:
· Influence of stud material (low – carbon steel material is prone to cause arc blow).
· Magnetic field interference (so it is also called “magnetic blow”).
· Interference from surrounding current – carrying equipment (such as the interference generated when the welding machine is working).
· Influence of the shape of the workpiece itself.
· Welding at the edge of the workpiece.
· During long – cycle gas – shielded welding.
· When the stud diameter is relatively large.
Arc blow is generally caused by external factors and has nothing to do with the quality of the welding machine itself.
Stud welding is a welding process that attaches threaded studs, pins (such as insulation nails), or washers (such as grounding terminals) to metal plates using an arc that requires no additional materials.
The term *arc requiring no additional materials* means the welding arc ignites and discharges without the assistance of other ignition mediums.
However, in some cases, protective media may be needed to improve molten pool formation. For example, gas-shielded stud welding requires inert gas to shield the arc from air, while ceramic ferrule stud welding uses a ceramic ring to shape the molten pool.
Stud welding can be divided into two main categories: *capacitor discharge stud welding* and *drawn arc stud welding*.
 Online
OnlineContact us to provide you with exclusive services!
Complete the information immediately to provide you with exclusive services!
Back to Top