The official foreign trade website of Hongbai Technology has been officially launched!


如果您打算开设自己的在线商店,请记住,收集客户数据需要HTTPS,因此请务必在启动您的网站之前购买 SSL 证书(否则您必须将 HTTP 重定向到 HTTPS,这可能会变得很复杂)。您还需要考虑为您的 网站使用和隐私条款以及退款政策创建页面。
当然,这还不包括在您所在地区(国家、州、省等)销售产品和/或服务所需的备案文件。
580+ employees
our products are widely used in FAW-Volkswagen, SAIC-Volkswagen, BYD, Chery, Tesla, Geely, Great Wall, Dongfeng Nissan, GAC-Toyota, FAW-Toyota, NIO, Xiaopeng, Ideal, Chang’an, SERES, Hongqi, Dongfeng Passenger Vehicle, Liuzhou Wuling, Lucky Harvest, Kasma, Minth Group, NORINCO Group, and other domestic mainstream automotive brands and parts suppliers and have won good market reputation.
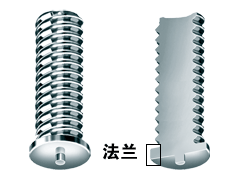 A flange refers to a raised edge around the front end of a stud. Usually, energy storage studs and short-cycle studs have flanges, while long-cycle studs do not.
A flange refers to a raised edge around the front end of a stud. Usually, energy storage studs and short-cycle studs have flanges, while long-cycle studs do not.
Since the molten pools in energy storage stud welding and short-cycle stud welding are relatively shallow, the presence of the flange edge can increase the welding cross-sectional area and improve the welding strength of the stud.
The phenomenon that the arc column of the arc deviates from the stud axis is called the arc blow phenomenon.

The picture shows the magnetic blow phenomenon that occurs during short-cycle pulsed arc welding.
When arc blow occurs, one side of the stud will melt intensely, resulting in little or almost no weld on one side of the stud, while the weld on the other side is excessive, accompanied by the generation of pores. It may even cause the stud to be non – vertical, easily burn out the collet, and may also affect the welding strength.
Arc blow mostly occurs during long – cycle drawn arc stud welding. It hardly occurs in energy – storage stud welding and rarely occurs in short – cycle drawn arc stud welding. The longer the welding time, the greater the possibility of arc blow.
The following reasons may cause arc blow:
· Influence of stud material (low – carbon steel material is prone to cause arc blow).
· Magnetic field interference (so it is also called “magnetic blow”).
· Interference from surrounding current – carrying equipment (such as the interference generated when the welding machine is working).
· Influence of the shape of the workpiece itself.
· Welding at the edge of the workpiece.
· During long – cycle gas – shielded welding.
· When the stud diameter is relatively large.
Arc blow is generally caused by external factors and has nothing to do with the quality of the welding machine itself.
Stainless steel mirror panels and stainless steel brushed panels have very high requirements for welding marks. Generally, users require that no marks can be seen on the back side after welding from any angle, which is quite difficult to achieve.
During stud welding, a powerful current in an instant melts the metal at the tip of the stud. Although the tip is very small, it can generate a high temperature of several thousand degrees Celsius in an instant. This high – temperature in an instant is quickly transferred to the metal plate and then the plate cools down. The whole process lasts less than 1 second.
However, even in such a short time, the thermal expansion and contraction effect will occur, and the plate will undergo very slight thermal and cold deformation. Such micro – deformation is difficult to cover on mirror panels and brushed panels and can be found by careful inspection under light.
Solutions:
Increase the thickness of the plate: Through experiments, we found that welding M3 – M4 stainless steel studs on a 4 – mm – thick mirror panel can basically avoid deformation. It is difficult to ensure no micro – deformation for plates thinner than 4 mm (of course, different manufacturers have different acceptance levels for micro – deformation. Here, “no deformation” means that no deformation can be seen from any angle).
Re – grind and polish the plate after welding.
The electrical cabinet manufacturing industry is a major category in the sheet metal manufacturing industry. Generally, the thickness of the sheet metal does not exceed 3mm (most of the sheets are 1 – 2mm thick). It is recommended to use energy storage stud welders.
Welding characteristics of energy storage stud welders:
Shallow molten pool, low requirement for sheet thickness.
Instantaneous welding, minimal thermal deformation of the sheet, and no blackening on the back.
Suitable for a variety of materials, can weld low – carbon steel cold – rolled sheets, stainless steel sheets, aluminum sheets, brass/copper sheets.
Weldable stud specifications: M3 – M10.
Absolutely superior to spot welding and argon arc welding in terms of welding quality.
High welding speed. The manual welding speed can reach 5 – 20 studs per minute, and the automatic welding speed can reach up to 40 studs per minute.
Not only the electrical cabinet manufacturing industry, but also other industries that meet the above stud welding characteristics are also recommended to use it.
In some sheet metal industries, if the sheet thickness is over 2mm, there is no requirement for the back welding marks (double – layer sheets, or the back is hidden and invisible, or there is no impact on post – processing), and there are special requirements for welding strength, such manufacturers can also use arc stud welders.
Elevator manufacturing industry uses stud welders quite often, usually for the installation of elevator panels and decorative panels in other parts.
Welding characteristics of energy storage stud welders:
Shallow molten pool, low requirement for plate thickness.
Instantaneous welding, minimal thermal deformation of the plate, and no blackening on the back.
Suitable for a variety of materials, can weld low – carbon steel cold – rolled sheets, stainless steel sheets, aluminum sheets, brass/copper sheets.
Weldable stud specifications: M3 – M10.
Absolutely superior to spot welding and argon arc welding in terms of welding quality.
High welding speed. The manual welding speed can reach 5 – 20 studs per minute, and the automatic welding speed can reach up to 40 studs per minute.
The kitchen and bathroom, household appliance manufacturing industry also includes the manufacturing of medical equipment, ultrasonic equipment, door locks, etc.
Welding characteristics of energy storage stud welders:
Shallow molten pool, low requirement for plate thickness.
Instantaneous welding, minimal thermal deformation of the plate, and no blackening on the back.
Suitable for a variety of materials, can weld low – carbon steel cold – rolled sheets, stainless steel sheets, aluminum sheets, brass/copper sheets.
Weldable stud specifications: M3 – M10.
Absolutely superior to spot welding and argon arc welding in terms of welding quality.
High welding speed. The manual welding speed can reach 5 – 20 studs per minute, and the automatic welding speed can reach up to 40 studs per minute.
Stud welding is a welding process that attaches threaded studs, pins (such as insulation nails), or washers (such as grounding terminals) to metal plates using an arc that requires no additional materials.
The term *arc requiring no additional materials* means the welding arc ignites and discharges without the assistance of other ignition mediums.
However, in some cases, protective media may be needed to improve molten pool formation. For example, gas-shielded stud welding requires inert gas to shield the arc from air, while ceramic ferrule stud welding uses a ceramic ring to shape the molten pool.
Stud welding can be divided into two main categories: *capacitor discharge stud welding* and *drawn arc stud welding*.
 Online
OnlineContact us to provide you with exclusive services!
Complete the information immediately to provide you with exclusive services!
Back to Top